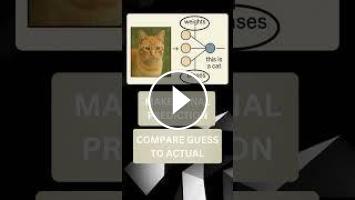
Neural networks take in data through an input layer. For example, if you show it a photo, the pixels go in as numbers. That data travels through hidden layers made of tiny units called neurons. Each neuron does a small calculation—kind of like making a guess—based on values called weights and biases, which tell the network how important each part of the input is.At the end, the network makes a final prediction—like “this is a cat.” If it’s wrong, it compares the guess to the correct answer and adjusts the weights. This learning process is called backpropagation, and it repeats with tons of examples. Over time, the network gets really good at spotting patterns and making accurate predictions.That’s how it can recognize faces, translate languages, or even help drive cars. Hit like and subscribe for more machine learning videos!
- Category
- Artificial Intelligence









Comments